Day 1 - Acute Kidney Injury
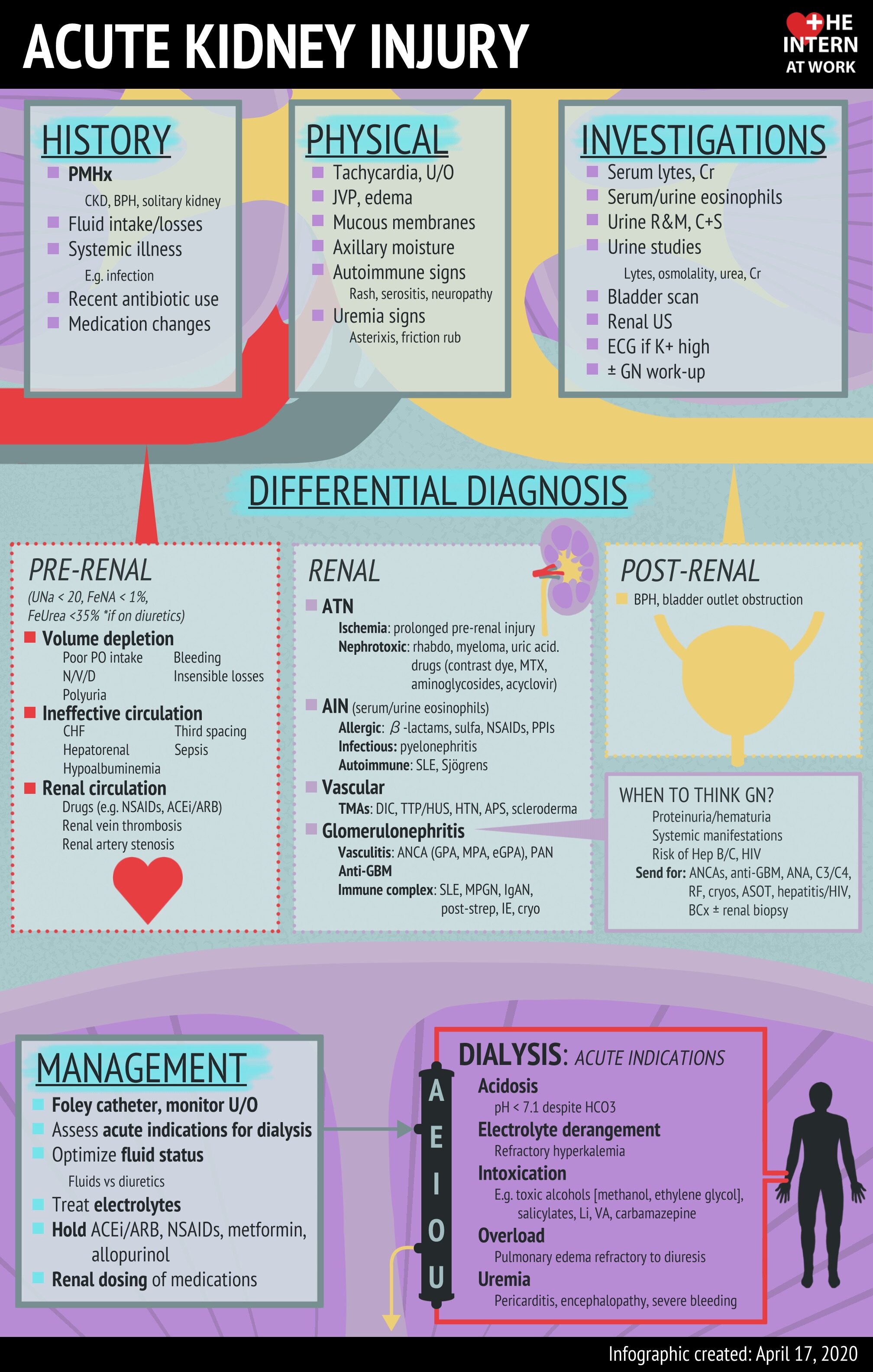
KDIGO definition: Rise in serum creatinine >1.5x baseline (presumed creatinine in past week), or >27 micromol/L over past 48 hours, or <0.5ml/kg/h of urine output for at least 6 hours
Indications for Dialysis:
Acidosis, Electrolyte abnormalities (Severe hyperkalemia), Intoxication (specifically toxic alcohols, aspirin), Overload, Uremia (Uremic encephalitis, pericarditis)
Work-Up:
Electrolytes, Bicarbonate, Urea, VBG, Urinalysis
Renal ultrasound
Urine electrolytes including urine urea may be helpful if indeterminate etiology
General Treatment Considerations:
Hold nephrotoxic medications
Monitor urinary output
Monitor for indications for dialysis
Post-Renal
Obstructive mechanisms
Consider in patients with BPH, obstructive intra-abdominal mass, intra-abdominal compartment syndrome
Neurogenic bladder
Treatment: Treat underlying cause, Foley for patients with urinary retention (neurogenic or obstructive)
Etiologies:
Pre-Renal:
Hypovolemia
Cardiorenal or hepatorenal states (Decreased effective circulating volume)
Medications: NSAIDs, ACE inhibitors, ARBs
UNa < 20
Treatment:
Hypovolemic states - Fluid resuscitation
Hypervolemic states - Diuresis
Renal:
Broad categories can be remembered with - Thank God It’s Vriday
Tubular:
ATN - most common cause of tubular AKI
Drug induced
Treatment:
Supportive care
Monitor for post-ATN diuresis
Dialysis if required
Glomerular:
Glomerulonephirits
‘Active’ urine with proteinuria, hematuria
Patients can also present with AKI, hypertension, pulmonary infilitrates, hemoptysis and other systemic manifestations of underlying ethology of GN
Glomerulonephropathy
Tends to have very mild creatinine elevation, but has significant proteinuria, defined as >3.5g / 24 hours
Treatment is targeted to underlying cause - Nephrology consultation recommended
Interstitial:
Acute interstitial Nephritis
May present with peripheral eosinophilia
Urine eosinophils helpful for diagnosis but may not be readily available
Treatment: Remove offending drug
Vascular
Reno-vascular occlusion including MAHA, renal vein thrombosis
Treatment: Targeted to underlying cause