Day 5 - ACLS
Don Airborne PPE prior to starting any BLS/ACLS protocol
Wear an N95 mask, limit number of people in the room to only those strictly necessary
Avoid aerosol generating procedures
Airway should be addressed only by an experienced specialist
No bag mask ventilation
Pause CPR during intubation
Important Roles to Establish during Code Blues
Code Leader - stands at the head of the bed
RN to establish IV access
Ideally either IO access or 2-3 large bore IVs
RN to administer medications
Timer/Recorder - needs to announce pulse check every 2 minutes
CPR line-up - monitor closely for fatigue and swap out if CPR quality is deteriorating
Airway specialist
Usually includes anesthetist/critical care physician + respiratory therapist
Pulse checker
Should always have hand on femoral pulse even during CPR
Cardiac monitor/Defibrillator manager
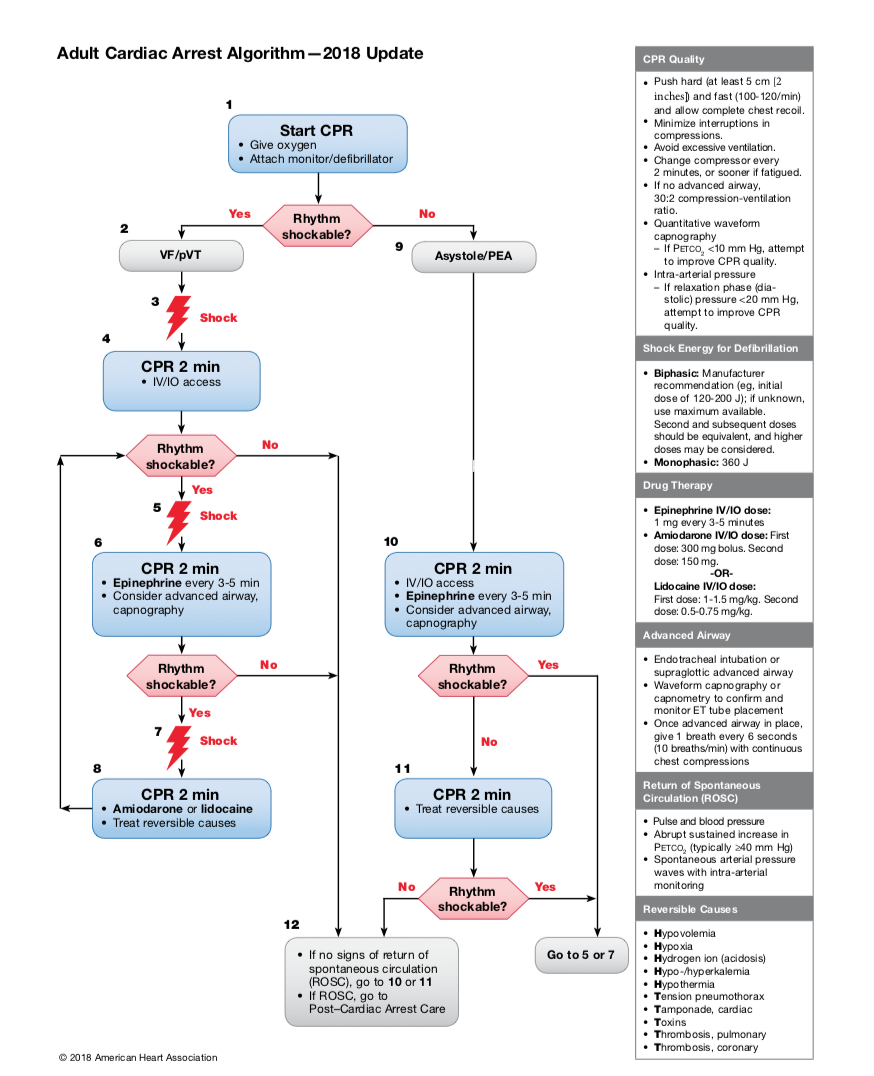
Identify and treat any reversible causes (Hs &Ts)
Hypovolemia - give volume
Hypoxia - supplemental oxygen/intubation
Hydrogen ions (acidosis) - give bicarbonate
Hypo/hyperkalemia - calcium gluconate, D50W & 10units IV insulin to shift (if hyper)
Hypothermia - rewarm
Tension pneumothorax - needle decompression/chest tube insertion
Tamponade (cardiac) - pericaridiocentesis
Toxins
Thrombosis (pumonary) - thrombolytics
Thrombosis (coronary) - thrombolytics
2018 AHA updates to ACLS algorithm
Amiodarone OR lidocaine can be used for VT/VF arrest unresponsive to defibrillation
The routine use of magnesium for cardiac arrest is not recommended
There is insufficient evidence to use beta blockers after achieving ROSC
There is insufficient evidence to support or refute the routine use of lidocaine early (within the first hour) after ROSC.